1. Graphene saturable absorbers
Saturable absorbers (SA) operating at terahertz (THz) frequencies can open new frontiers in the development of passively mode-locked THz micro-sources. We developed THz SAs by transfer coating and inkjet printing single and few-layer graphene films prepared by liquid phase exfoliation of graphite. Open-aperture z-scan measurements with a 3.5 THz quantum cascade laser show a transparency modulation ∼80%, almost one order of magnitude larger than that reported to date at THz frequencies.
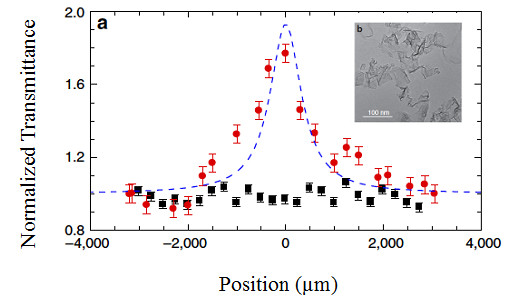
(a) z-scan normalized transmittance of a water-based graphene saturable absorber probed with a 3.4 THz QCL (b) Transmission electron microscopy images of few-layer graphene flakes from water based inks.
References:
1. V. Bianchi, T. Carey, L. Viti, L. Li, E.H. Linfield, A.G. Davies, A. Tredicucci, D. Yoon, P.G. Karagiannidis, L. Lombardi, F. Tomarchio, A.C. Ferrari, F. Torrisi & M.S. Vitiello, “Terahertz saturable absorbers from liquid phase exfoliation of graphite” Nat. Commun. 8, 15763 (2017).
2. Intersubband polariton based saturable absorbers
Intersubband (ISB) transitions in semiconductor multi-quantum well (MQW) structures are promising candidates for the development of saturable absorbers at terahertz (THz) frequencies. We developed polaritonic saturable absorbers at THz frequencies and exploit amplitude and phase-resolved two-dimensional (2D) THz spectroscopy on the sub-cycle time scale, to observe directly the saturation dynamics and coherent control of ISB transitions in a metal-insulator MQW structure.
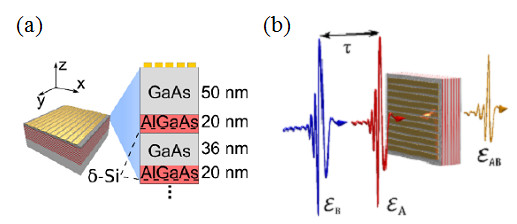
(a) Schematic diagram of the THz saturable absorber structure (b) Experimental principle showing the two identical THz pulses with fields eA and eB and delayed by a time 𝜏, which prepare and interrogate the structure’s nonlinear response eAB.
References:
1. J. Raab, C. Lange, J.L. Boland, I. Laepple, M. Furthmeier, E. Dardanis, N. Dessmann, L. Li, E.H. Linfield, G.A. Davies, M.S. Vitiello & R. Huber, “Ultrafast two-dimensional field spectroscopy of terahertz intersubband saturable absorbers”, Optics Express 27, 2248 (2019).
3. THz waveguide adapters for efficient radiation out-coupling from double metal THz QCLs
We developed a novel approach to couple THz radiation from a double-metal QCL into an on-chip hollow rectangular waveguide feeding a triangular horn, with the specific aim of optimizing the optical beam divergence. The conceived novel extractor is composed of three parts: a series of slits patterned at the end of the laser top contact (slit coupler), a metallic waveguide section (feeder) assembled on top of the laser itself, and an adiabatic expansion of the feeder, forming a horn that radiates into an optical fiber or, alternatively, into free space.
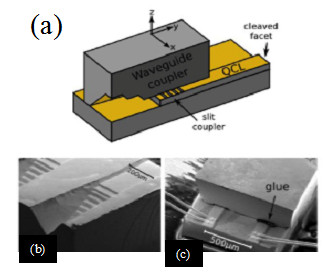
(a) Device schematics: yellow areas indicate metallized surfaces, grey area correspond to GaAs. (b) Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the cleaved chip containing two waveguide couplers; (c) SEM image of the final assembly, taken from the cleaved facet side.
References:
1. F. Castellano, H.L. Li, E.H. Linfield, A.G. Davies, H.E. Beere, D.A. Ritchie & M.S.Vitiello, “THz waveguide adapters for efficient radiation out-coupling from double metal THz QCLs” Optics Express, 23, 5190 (2015).